TECHNOSPHERE SAFETY
Introduction. One of the health-saving resources for the working population is the improvement of the occupational safety system and prevention of occupational injuries (OI). Systematic scientific research in this field remains relevant as it helps to understand the interrelationships between the causes and consequences of OI in different sectors of economic activity. In recent years, there has been a lack of research on the structure and dynamics of OI in the Republic of Crimea (RC), and its indicators have not been compared. The aim of this study was to conduct a comparative analysis of Crimean and all-Russian dynamics of occupational injuries over a five-year period from 2017 to 2021 in order to identify trends and develop strategies for improving production safety.
Materials and Methods. Methods of systematization of scientific literature on the issue of OI were employed. Statistical data on the state of OI in the Republic of Crimea and the Russian Federation were analyzed and compared. The results were graphically presented in the form of histograms. Additionally, the positions of the republic in the official ratings on compliance with labor legislation were taken into consideration.
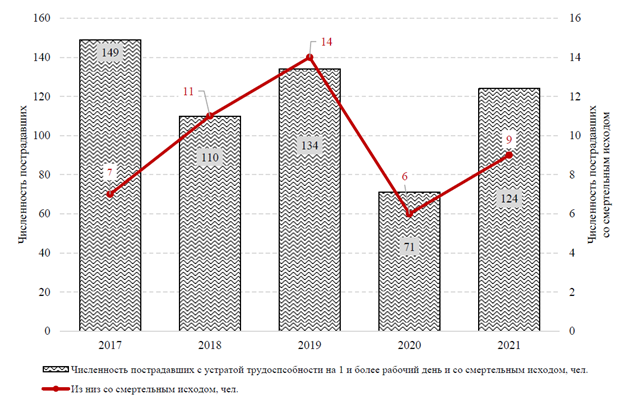
Results. The analysis of statistics has made it possible to compare the structure and dynamics of OI indicators in the Republic of Crimea with similar data on the national average. Regional differences in occupational injury rates have been identified. In 2017–2021, the number of fatal injuries per 1 000 workers increased in the country, and in Crimea the problem was more acute than in the average for Russia. According to the results for 2021, construction was the most hazardous type of activity in the Crimean region, while mining was the most dangerous one in the Russian Federation. The relative rates of occupational injuries (per 1 000 employees) in the region were lower than the national average. At the same time, the proportion of fatal injuries in Crimea was 1.5–2 times higher than the national average. The highest level of fatal injuries in Crimea was recorded in 2018–2019, likely due to increased construction activity. Injury rates were increasing, while the costs of occupational safety measures were also rising. At the same time, in 2021, the amount of funds allocated to labor protection in Crimea was approximately 1.7 times lower than the similar national average (per employee).
Discussion and Conclusion. It is advisable to use data on occupational injuries in the Republic of Crimea to develop scientifically grounded recommendations for improving the regional occupational safety system. These results are partially influenced by the integration of Crimea and are presented in comparison with all-Russian indicators. Therefore, the findings of this scientific work can be applied more broadly when developing a strategy for labor protection in other regions of the Russian Federation.
Introduction. Plant pollen causes various allergic reactions in humans, including respiratory diseases, immune system disorders, bronchitis, conjunctivitis, dermatitis, and hay fever. These diseases affect up to 30% of the world's population. In large cities, trees and shrubs used in landscaping are significant sources of allergenic dust. Despite this, the greening of cities worldwide often occurs without considering the allergenic properties of plants. With the development of proteomics, it has become possible to assess the degree of allergenicity of proteins that make up plant pollen in detail. Based on this information, a scale of potential allergenicity for woody plants has been developed. The aim of this study is to assess the allergenic potential of woody plants in the urban flora of Rostov-on-Don.
Materials and Methods. The object of the study was trees and shrubs used in the landscaping of Rostov-on-Don. The analysis of floristic data was based on the materials obtained during field work in 2023 on the territory of Rostov-on-Don. The author also used the lists of the city's dendroflora compiled between 2007 and 2022. The assessment of the potential allergenicity of woody plant species was conducted on a five-point scale, with 0 indicating plants that did not pose an allergic hazard, 1 indicating a low allergenicity level, 2 indicating a medium class, 3 indicating a high level, and 4 indicating a very high level of allergenicity.
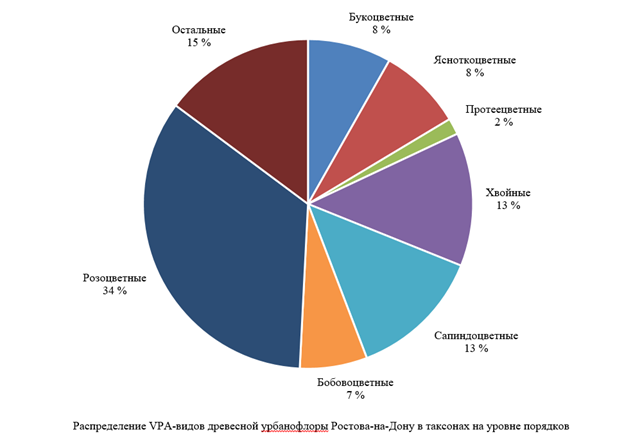
Results. In the flora of woody plants in Rostov-on-Don, 61 species of potentially allergenic plants were identified, posing varying levels of danger to human health. The share of all types of potentially allergenic woody plants was 30% of the total number of urban woody flora species in the city. The most powerful sources of allergenic pollen included nine species (Fraxinus Excelsior, Betula Pendula, B. Verrucosa, Platycladus Orientalis, etc.), which posed the greatest threat of hay fever and other allergic reactions. As a rule, these were typically wind-pollinated plants that produced maximum amounts of pollen. The list of potentially allergenic species included a significant number of adventitious species (24 species), which made it difficult to control their spread. A taxonomic analysis of potentially allergenic species was carried out at the order level, for which specific protein reactions were identified and detailed approaches to the prevention and treatment of hay fever were developed. The orders Pinales and Fagales form the bulk of allergenic pollen in the winter-spring period.
Discussion and Conclusion. For the first time, studies were conducted on the allergenic activity of urban woody flora in the southern regions of Russia. An assessment of their allergenic potential allowed us to determine the level of threat of allergic reactions in humans. The greatest danger comes from both allergenic and invasive species that can spread actively and increase in numbers. Representatives of the Pinales and Fagales orders have proven to be significant sources of allergenic pollen, as they often have high ornamental qualities and play a prominent role in design projects. In some cases, it may be possible to replace these cultures with less allergenic alternatives, such as representatives of the Rosales order, to reduce the risk of allergic reactions.
Introduction. Currently, there is a problem with the accumulation of large amounts of production waste. One type of this waste is excess activated sludge, which is a waste product from biological wastewater treatment that has a high moisture content. When excess activated sludge is deposited in beds, problems can arise related to changes in the gas-air environment, the release of unpleasant odors, as well as the contamination of groundwater and soil. Prolonged presence of sediment in sludge beds in oxygen-free conditions leads to its decay and deterioration of moisture-yielding properties. For these reasons, the development of new methods for disposing of large volumes of waste generated during wastewater treatment is essential. The aim of this research is to develop a technique for preliminary neutralization and thermal treatment of excess activated sludge using energy waste.
Materials and Methods. The work used excess activated sludge with a moisture content of 98.2% (waste of hazard class IV). Water treatment sludge (waste of hazard class V) was used as a reagent to increase moisture yield. For experimental studies on dehydration, a laboratory centrifuge Elmi CM-6M.01 was used. Tests were conducted under various conditions (500, 1 000, and 1 500 revolutions per second for 1, 2, and 3 minutes), and the value of centrifugation was determined as a criterion for moisture yield in the sludge. Fuel pellets were produced by rolling with technical lignosulfonate as a binding agent. Elemental analysis of the samples was conducted to study the possibility of thermal treatment using an EA 3 000 Euro Vector Analyzer.
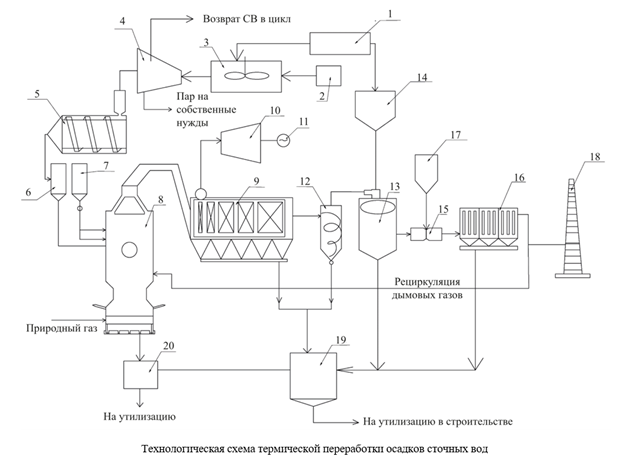
Results. A comprehensive technology has been developed to clean the resulting gas emissions from solid particles formed during the combustion of fuel pellets and remove them from the furnace in the form of fly ash along with the outgoing gases. This technology also removed sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and polychlorinated dibenzodioxins and dibenzofurans, while beneficially utilizing flue gas heat by reducing its temperature from 900–1 200°C to 140°C.
Discussion and Conclusion. The approach proposed in this article for the processing and disposal of large volumes of waste allows for the reduction of moisture content of excess activated sludge and the use of this waste as a secondary energy source. This method is environmentally friendly and addresses both technical and environmental challenges, such as the effective recycling of industrial waste and reducing the anthropogenic impact on soil, air, and groundwater. It also provides an opportunity to generate additional electrical and thermal energy through thermal utilization of waste. The results of this work indicate that it is possible to integrate the use of various types of industrial waste (sewage sludge, water treatment waste, and pulp and paper industry waste) as secondary energy sources. These findings have practical implications for enterprises in both the municipal and industrial sectors with wastewater treatment facilities.
Introduction. The increasing anthropogenic impact on water bodies necessitates integrated solutions to assess environmental risks. Literature describes the stages of risk assessment, the possibilities of environmental management, and expert analysis, while risk modeling in this field is being investigated. However, the potential for predicting risks to water quality and biodiversity during frequently performed hydraulic engineering works such as dredging has not been fully explored. The relevance and practical significance of such an approach are evident. This study aims to develop a mathematical model and software package that can assess risks to species diversity of the ecosystem of a shallow reservoir ecosystem during work in its water area.
Materials and Methods. The starting point for the simulation was a description of the movement of water masses based on the Navier-Stokes equations and the continuity equation at variable density. We used the diffusion-convection equation to predict the transfer of suspended and dissolved particles, as well as to assess the impact of impurities during eutrophication. To create the algorithm, we utilized the terms and definitions defined by the state standard for risk management in emergency situations.
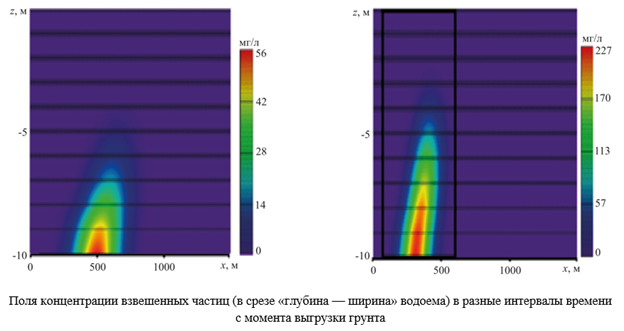
Results. To test the solution, we took data on hydro-mechanical work in the port area of Arkhangelsk. We visualized the concentration fields of suspended particles 0, 15, 30 and 45 minutes after the soil was unloaded. It was found that during the settling of the suspension, the area of its distribution expanded significantly, and this was fully consistent with the data of field experiments during dredging. We calculated and tabulated the volumes of contaminated water at soil dumps in three sites (with a single discharge and in total). To assess the risks to the Sea of Azov, we used the maximum concentrations of pollutant (copper) obtained through measurements, modeling and remote sensing of the Earth. In tests to determine the potential danger of the substance, we assumed that its concentration caused a reaction in 50% of organisms. For fish, the potentially dangerous concentration was 4 mg/l with a duration of 96 hours of exposure. For zooplankton — 50 mg/l and 48 hours. For microalgae, 20 mg/l and 72 hours. The normalized risk value Rn ≈ 0.52 was obtained. The risk of copper concentration of 80 µg/l in the waters of the Azov Sea was recognized as significant. A tendency towards increasing salinity and stratification of water masses in terms of oxygen content has been identified, consistent with the findings of expeditionary research.
Discussion and Conclusion. The developed approach has allowed us to assess the change in the quality of the waters of the Azov Sea and describe some transformations of the water area. Specifically, we are talking about the distribution of suspended particles and areas of their deposition. These processes can lead to changes in the bottom topography, which in turn can reduce the species diversity of the ecosystem.
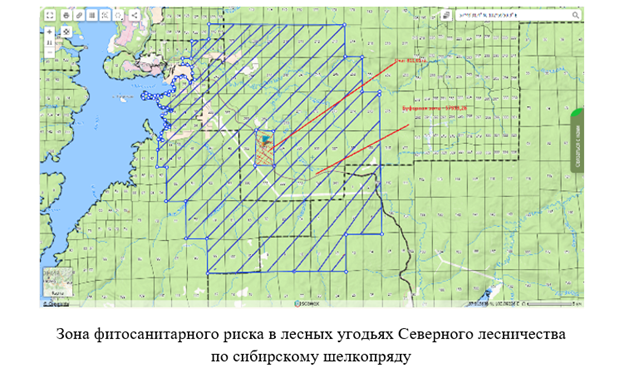
Introduction. Timber export plays a significant role in the budget of the Irkutsk region. To ensure the continued and sustainable use of forest resources, it is essential to implement preventive measures for forest conservation. One such measure is the analysis of phytosanitary risk, which helps to identify potentially harmful insects and determine the likelihood of their introduction and spread, as well as the potential economic consequences. From the perspective of applied riskology, it is necessary to carry out a predictive assessment, calculate the acceptability of risks and develop methods for managing them, combining economic and monitoring approaches. The aim of the presented work was to assess and predict phytosanitary risks in the Irkutsk region and potential damage to forestry and the economy, as well as to develop measures to reduce them.
Materials and Methods. For this analysis, we used the results of forest surveys conducted in the Irkutsk region in 2021–2023 with the participation of the authors of this article. These surveys included the identification and detection of harmful insects, as well as the determination of their distribution areas according to GOST 34 309–2017 and the methodology approved by the phytosanitary control authority. Additionally, data from official statistics from the Federal Customs Service of Russia for 2021–2023 were used.
Results. We found populations of quarantine pests listed in the Unified List of Quarantine Objects of the Eurasian Economic Union in the forests of Ust-Ilimsky district, such as Monochamus sutor, Monochamus sartor, Monochamus galloprovincialis, Dendrolimus superans. We calculated the phytosanitary risk and assessed the quarantine phytosanitary zone, taking into account the buffer zone.
Discussion and Conclusion. The results of the analysis suggest an unfavorable phytosanitary situation in the studied areas. The high infestation of the detected harmful insects in the Ust-Ilimsky district compared to the reference areas indicates the potential for quarantine zones and losses for loggers. To manage phytosanitary risks, it is important to select options that are effective in reducing the spread of quarantine organisms and minimizing risks to an acceptable level. Sanitary logging with timely removal of wind-damaged and fire-affected trees, as well as the use of pheromone traps and biological products, are environmentally friendly options for managing phytosanitary risks.
MACHINE BUILDING
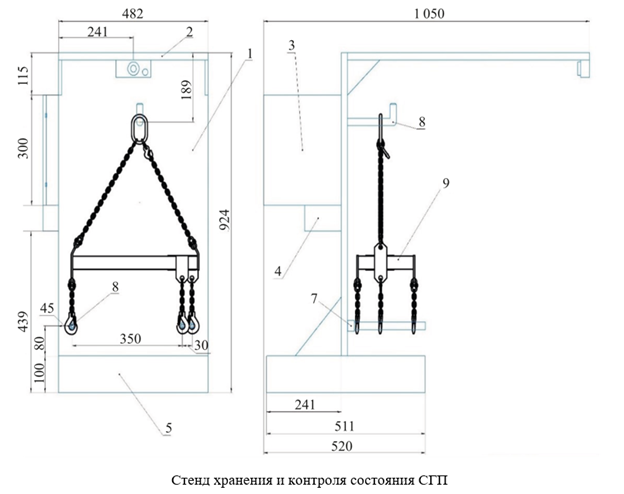
Introduction. The malfunction of removable load-handling devices (RLHD) poses significant production risks. That is why research in this field is relevant. The problem has often become a topic of scientific investigation. The authors propose using artificial intelligence more extensively to monitor the state of RLHD. This paper presents a study on how to improve the machine vision model to better identify the absence of locks on RLHD hooks. A probable occurrence of such an issue in production is noted. A storage and monitoring system for RLHD condition is proposed. The aim of this study is to demonstrate the potential for further training of neural networks to significantly enhance the efficiency of RLHD monitoring, ensuring their safe use.
Materials and Methods. The work is based on the results of a survey conducted at the LLC “KZ Rostselmash” plant from 2022 to 2023, involving 144 RLHD. Mathematical statistics methods were used to process the data. A neural network model previously trained using the YOLO computer vision algorithm was studied. It was retrained taking into account the norms of the rejection of RLHD, specified in federal rules and standards. Images of RLHD with defects and missing parts were collected from these sources and used to create a training database. The database was expanded by augmentation. The Roboflow platform was used for work.
Results. The array of images used for further training of the neural network was divided into three samples: training (88%), validation (8%) and test (4%). These samples were used to train and validate its results. The training was completed after 260 epochs, with a steady increase in accuracy. The neural network model of computer vision obtained in this way automatically detected a common defect in the RLHD hook — the absence of a lock. Its performance was assessed using three indicators: average accuracy (94%), prediction accuracy (88.8%) and response (89.2%). The neural network could receive images from a video camera in real-time and recognize hook defects. During the RLHD inspection at the Rostselmash plant, a grab for lifting engines was found to have all three hooks defective — without locks. To avoid such situations, at the end of work, it was recommended to place the RLHD on a special stand equipped with a microcontroller device that could monitor for a number of potential issues using radio frequency identification.
Discussion and Conclusions. The main goal of this proposed solution is to detect and address signs of non-compliance with the established standards. This task can be implemented in facilities that use lifting equipment. In this case, the timely noticed RLHD defects will allow preventing production incidents. As a result, material damage can be reduced and injury statistics improved.
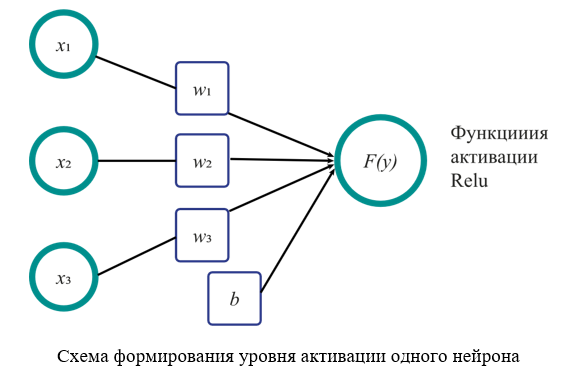
Introduction. Currently, artificial neural networks (ANN) are successfully used for technical diagnostics of steel ropes. Expensive software products with an adapted neural network implementation environment, such as STATISTICA, Amygdala, MatLab Simulink, are often used for this purpose. The most affordable way to build and train an ANN, from a financial point of view, is to write your own program code using interactive libraries such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn. However, such libraries are not fully adapted for building an ANN, and to use them you need to have basic programming skills. As a result, the quality of an ANN depends not only on its architecture, training data, and composition, but also on the environment in which it is built. The aim of the work was to compare the quality of the ANN, built and trained by various methods according to the criterion of test network performance, confidence levels for assessing the technical condition of the rope, as well as the complexity and speed of training. For this purpose, new software has been developed to solve the problem of assessing the technical condition of a steel rope using a combination of various rejection indicators.
Materials and Methods. The basis for an ANN training was a statistical database of typical damages of steel ropes and, an expert assessment of the technical condition of steel ropes. The software was written in the Python programming language. Various methods of programming a neural network were presented: an ANN built on the basis of the STATISTICA software package and an ANN built using the interactive Scikit-learn library. Ten test samples were prepared to verify the operation of the ANN. The ANN quality was assessed based on the test network performance and confidence probabilities (activation levels of the “winning” neuron) of determining the technical condition of the rope.
Results. The construction of the ANN using the interactive library Scikit-learn showed a relatively high complexity of construction and a relatively low learning rate of the ANN. Test performance of the network, with a test sample size of ten, turned out to be the same for both built ANNs. At the same time, there was a difference in the indicator of the average confidence level for determining the technical condition of a steel rope between the results of the ANN built on the basis of the STATISTICA software package and the ANN built using the Scikit-learn interactive library.
Discussion and Conclusion. The results showed that the ANN built using the STATISTICA software package with the same architecture and network learning parameters had more optimal software algorithms according to the criteria of confidence probability and network learning speed in comparison with the ANN built using the free Skicit-learn library. However, the indicator of the ANN test performance turned out to be the same for both ANNs. This result justified the use of TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Skicit-learn libraries by the world's leading research and commercial centers in the field of artificial intelligence. The obtained scientific result allows us to numerically evaluate and compare the quality of an ANN having the same architecture and learning parameters, but built using different methods. This will be useful for future scientific research in the field and for selecting the optimal environment for constructing ANNs in industrial applications.
CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGIES, MATERIALS SCIENCES, METALLURGY
Introduction. The production of alloyed powder steels continues to be one of the most promising areas in domestic powder metallurgy. This is due to the high level of performance characteristics and the wide range of products that can be produced. Creating materials with desired properties is a complex process that involves various phenomena. One of these phenomena is the diffusion alloying of iron-based powder steels, which plays a special role in this process. The creation of alloyed powder steels in the Fe-NiO and Fe-Ni systems is important for metallurgy and metalworking, as they are used for coating and sintering to obtain materials with specific properties. In addition, the diffusion of nickel in iron during heat treatment is considered to improve material properties. Recent advances in the study of mutual diffusion are associated with the investigation of homogeneous systems. However, mutual diffusion even in single crystals always occurs under spatially inhomogeneous conditions. The modern literature has not sufficiently studied the mutual diffusion in two- and multi-component powder systems. Therefore, the aim of this work is to determine the effect of diffusion alloying with nickel and nickel oxide of iron-based powder steel on the processes of obtaining powder materials. Within the framework of this goal, the following tasks were set: to investigate the diffusion processes of interactions between pairs in the Fe-NiO and Fe-Ni systems, as well as to study technological modes of sintering and reducing annealing of samples in order to achieve maximum mechanical properties that would ensure the formation of a high-quality product.
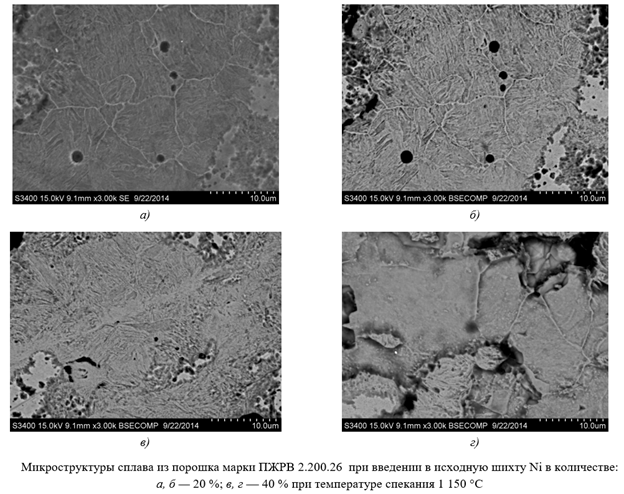
Materials and Methods. The work used iron powder of the PZHRV 2.200.26 brand manufactured by PJSC Severstal (Cherepovet) and carbonyl nickel powder PNK-UT3, obtained by the electrolytic method or splitting nickel salt with an aqueous solution, according to GOST 97922–97. Before use, the powders were tested using a universal laser particle size measuring device model FRITSCH ANALYSETTE 22 MicroTecplus and a Beckman COULTER No. 5 submicron particle analyzer. A two-cone mixer RT-NM05S (Taiwan) was used to prepare the charge. Pressing was carried out on a hydraulic press model TS0500–6 (China) in laboratory molds. Samples were obtained by pressing pre-hardened 3 mm diameter powder pins into a carbonyl nickel or NiO charge with a dispersion of 5–10 microns. Recovery annealing was carried out in a SNOL 6.7/1300 laboratory muffle furnace at 700°C, followed by annealing-sintering at temperatures of 1050, 1150 and 1250°C in a hydrogen atmosphere for 9 hours. Microstructural analysis was performed using a NEOPHOT-21 optical microscope. A Hitachi S-3400N scanning electron microscope was used to study the fine structure of the material. The distribution of element concentrations in the Fe-Ni diffusion zone was studied by local X-ray spectral analysis using the Kamebaks installation.
Results. The studies showed that the porosity of the powder component after pressing was 12%. Diffusion in the iron-nickel powder system was 5–10 times higher when using carbonyl nickel compared to oxide. It was also found that high diffusion rates of reduced nickel led to faster and more uniform penetration of alloying elements into the material. The dependences of the distribution of nickel concentration and its oxide content after sintering were determined, as well as the indicators of diffusion interaction between iron, nickel, and nickel oxide during annealing, where nickel oxide was reduced and sintering occurred at different temperatures.
Discussion and Conclusion. The analysis of the results obtained indicates a different intensity of diffusion processes in powder-alloyed steels. This can be explained by both the distortion of the crystal lattice of the starting materials and the increased segregation of defects, such as defective zones, that are formed during compaction of the material. This approach to studying two-component diffusion allowed us to compare the intensity of element diffusion redistribution depending on chemical composition and temperature, and to estimate the effective activation energy of diffusion. As a result of our studies, we have established quantitative parameters for the distribution of nickel concentration in the iron matrix, depending on sintering temperature, which affects the formation of high-quality materials. The research results obtained are of interest to specialists in powder metallurgy and heat treatment, as they can be used in the development of new multicomponent alloys.
Introduction. Failure of equipment, specifically pipes in the oilfield complex, due to the development of corrosion processes leads to numerous losses, destruction of expensive components, disruption of technological processes and, as a result, environmental damage. The use of anticorrosive coatings as an internal protection of oilfield pipes offers many advantages and can significantly reduce the rate of corrosion, but does not provide a complete solution to this problem. Destruction of internal anticorrosive polymer coatings (IACPC) occurs for numerous reasons. The causes and mechanisms of destruction are insufficiently investigated. Therefore, the aim of this work was to analyze the destruction of internal anticorrosive polymer coatings using practical examples, which made it possible to form and identify the main causes of damage and degradation of coatings during operation.
Materials and Methods. A complex of laboratory studies was carried out to study the damage to internal polymer anticorrosive coatings during operation and to establish the main causes of destruction. The initial phase of the investigation involved a detailed examination of the materials related to the accident circumstances, including the operating conditions of the coated pipeline (composition of the operating medium, temperature, pressure, and presence of mechanical impurities), operation time, and type of polymeric material used. The second phase involved laboratory testing of the coating, which included the determination of layer thickness, dielectric continuity, adhesive strength (by the normal separation method), investigation of thermokinetic properties by means of differential scanning callometry (DSC), study of the coating structure using scanning electron microscopy.
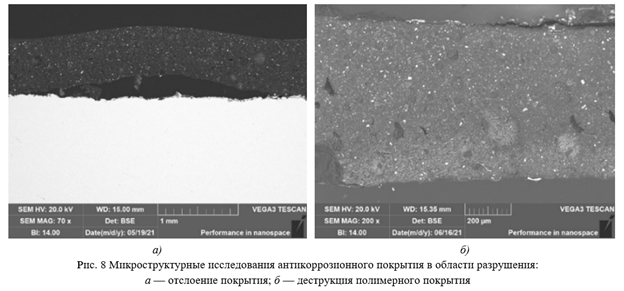
Results. Practical examples of the destruction of internal anticorrosive coatings of oilfield pipes were analyzed. For each case, characteristic signs of degradation of the anti-corrosive coating were identified. Changes in the microstructure of the coatings, as well as the formation of corrosion products, were observed depending on the type of destruction. The focus was on studying the degree of polymerization of the coating, both using the traditional method of determining the ΔTg parameter using DSC, and based on indirect signs detected during microscopic studies.
Discussion and Conclusion. The practical cases of damage to the internal anticorrosion coating of pipes of the oil and gas complex considered in the article allowed us to divide the causes of destruction into three groups: operational, technological and defects during transportation, storage and construction and installation works. Based on these findings, we have formulated recommendations for manufacturers to ensure maximum performance from their coatings. It is noted that the compliance with the presented recommendations makes it possible to obtain internal anticorrosive polymer coatings with a minimum guaranteed lifespan of 15 years, as demonstrated by the successful operations of pipelines in Western Siberia, such as those operated by Surgutneftegaz PJSC and LUKOIL – Western Siberia LLC.